-
Products
-
Industries
-
Company
-
Resources
-
Pricing
As of March 2024 we have renamed Apexchat to Blazeo. We are excited to share the next part of our journey with our customers and partners.
The name ApexChat implies that we are primarily a chat company, which is no longer true. Now we have many offerings, such as call center services, AI, Appointment setting, SMS Enablement, Market Automation, and Sales acceleration (Q2 2024), that go beyond chat. The new name will not only allow us to convey the breadth of our offering but will also better convey our company’s mission and values.
Blazeo, which is derived from the word Blaze, evokes a sense of passion, speed, and energy. A “Blaze” is captivating, illuminates, and represents explosive growth. Blazeo encapsulates our mission to ignite such growth for our customers and partners by delivering innovation with passion, speed, and energy.
Cybersecurity and cyberattacks have become one of the top concerns for small-to-medium-sized businesses in 2020.
Most cyberattacks can rack up serious damages to your business's reputation and financial stability.
Some examples include:
Businesses are popular targets for cybercriminals because of their ever-growing volumes of valuable customer data - such as intellectual property (IP), employee and client personally-identifiable information (PII), financial records and much more.
In addition, a 2017 study published by the Better Business Bureau (BBB) found that 28% of small businesses reported a lack of resources as their top obstacle to achieving cybersecurity goals.
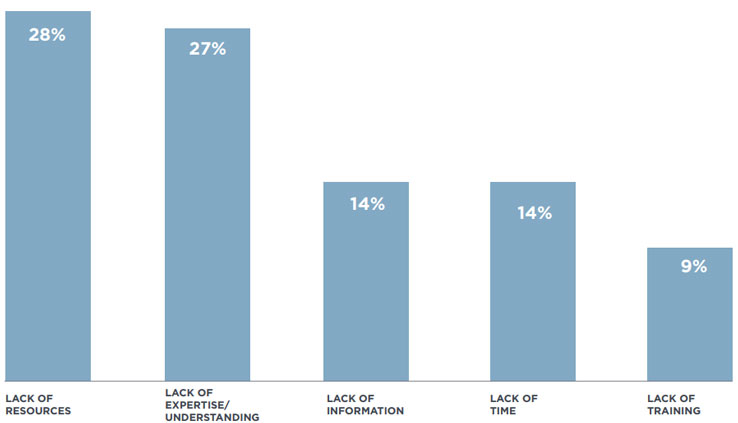
The five main factors listed above are what we'll tackle in this post, as many SMB's struggles relate to feeling unprepared or overwhelmed when it comes to cybersecurity.
Here are some of the best cybersecurity trends and tips for small-to-medium-sized businesses to combat cyberattacks in 2020.
Up until this year, cyber-attacks such as data breaches and DDoS have been associated with large businesses and enterprises.
It makes sense for criminals to target them since top corporate officials have the most to lose in terms of IP wealth, capital and other valuable data.
Accenture’s 2017 Cost of Cyber Crime Study chart below is a great example of how costly cyberattacks can be for many industries.

Where most businesses falter is assuming they are immune to attacks because of their size relative to these larger companies.
Due to recent attacks, large businesses are continuing to increase cybersecurity spending (in areas like cybersecurity consulting). This means that cybercriminals are targeting newer, weaker targets - small-to-medium-sized businesses (SMB).
What are your business’ cybersecurity priorities? If you’re not sure, it’s time to find out. To help you get started with your cybersecurity protection strategy, here are the top priorities you should address to protect your business from cyberattacks.

Employee training is one of the most important security breach prevention methods to implement for your business.
It’s important to note that the vast majority of internal cyber vulnerabilities are accidental or unintentional. Employees are the foundation of your operation, and training them on some basic cybersecurity doesn’t cost very much nor does it consume much of your employees’ time.
With that being said, employees can be unpredictable and no matter how many firewalls and cybersecurity software you employ, your employees are still able to bypass them all.
Training should consist of establishing a common understanding of what not to click on, what to avoid downloading, how to keep your companies data safe, and how to properly maintain their passwords. An example of password management could be not using the same password for multiple accounts, no matter how easy it is to remember.
Every employee is different, so outlining the basic user training and understanding, in the beginning, can go a long way in keeping your business protected in the long run.

MFA sometimes referred to as two-factor authentication or 2FA, is a security enhancement that allows you to present two pieces of evidence – your credentials – when logging in to an account.
Usually, your credentials fall into three distinct categories: something you know (like a password or PIN), something you have (like a smart card), or something you are (like your fingerprint).
For MFA, you’ll need to use two of those categories to enhance your security. Entering two different passwords would not be considered multi-factor.
In terms of your business, MFA is a great security measure to implement for your email network or CRM infrastructure where most of your data lives.
This also reinforces your employee training from earlier. Even though you did user training, the passwords your employees are using are likely the same passwords they use for their employee records and all other work systems, and possibly even their home systems (other places you cannot control).
It’s human nature to do the same tasks that are proven to work, and if an employee doesn’t realize they are using a vulnerable password, they are probably going to use it until it’s too late.
MFA makes using those passwords much more difficult to breach, adding a separate layer of protection to your business.

Knowing your biggest weakness can also be your biggest strength.
Understanding where your vulnerabilities lie allows you to make good business decisions on what you want to remediate. If you don’t understand your problems, you can’t make well-informed decisions about your risks.
Cybersecurity vulnerability assessments are a very easy way of going through your network — by using a few automated tools — and finding the most common breaches or the most prevalent vulnerabilities.
These tools analyze the different platforms you use for things like systems not being patched, systems lacking anti-virus, systems having local admin rights that they shouldn’t have, etc.
While these things are minor in the grand scheme of security, cybersecurity vulnerability assessments will help outline larger security holes in your network.
Some examples of this include patching, closing vulnerabilities — such as ports in your firewall that you’re not even using — and other measures that reduce your exposure.
Cyberthieves are looking for easy targets, and for them time is everything when trying to breach your network. If you make their lives a little bit harder, they’re more likely to move on to the next victim.
There’s a lot of items to account for when updating your business's cybersecurity, so we’ve compiled a quick checklist of items you should consider when creating your cybersecurity plan.
End-points are vulnerable applications that hackers and other cybercriminals are targeting in order to attack your business. End-points are specific hardware, software and any other systems that make up your overall IT system. Most SMB’s end-points include their mobile devices, networking systems (switches, routers, servers, etc) and computers. Below is a checklist to help you diagnose vulnerabilities:

Prevention Measures:



Cybersecurity for small businesses will vary, but with these safety steps, you’ll be better prepared for any future attacks on your business.
Remember, meeting your customers' cybersecurity expectations isn’t optional, it’s mandatory for any business operating online. Your customers expect you to protect their customer records, whether it be credit or debit card information, personal information or any other sensitive data.